Many a times we come across a scenario where we need to execute some code based on whether a Table exists or not. There are different ways of identifying the Table existence in Sql Server, in this article will list out the different approaches which are commonly used and it’s pros and cons. I prefer using the OBJECT_ID() function as it is easy to remember. Let me know which approach you use and reason for the same.
To demo these different approaches let us create a sample database with a table by the below script:
CREATE DATABASE SqlHintsDemoDB GO USE SqlHintsDemoDB GO CREATE TABLE dbo.Customers (CustId INT, Name NVARCHAR(50))
[ALSO READ] How to check if Temp table exists in Sql Server?
Approach 1: Using INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES view
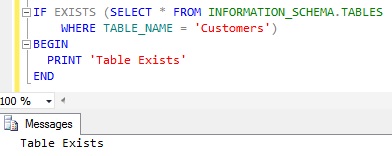
We can write a query like below to check if a Customers Table exists in the current database.
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
WHERE TABLE_NAME = N'Customers')
BEGIN
PRINT 'Table Exists'
END
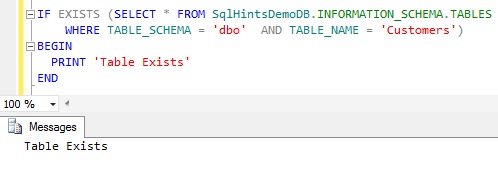
The above query checks the existence of the Customers table across all the schemas in the current database. Instead of this if you want to check the existence of the Table in a specified Schema and the Specified Database then we can write the above query as below:
IF EXISTS (SELECT *
FROM SqlHintsDemoDB.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = N'dbo' AND TABLE_NAME = N'Customers')
BEGIN
PRINT 'Table Exists'
END
Pros of this Approach: INFORMATION_SCHEMA views are portable across different RDBMS systems, so porting to different RDBMS doesn’t require any change.
[ALSO READ] How to check if a Stored Procedure exists in Sql Server
Approach 2: Using OBJECT_ID() function
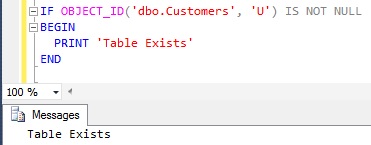
We can use OBJECT_ID() function like below to check if a Customers Table exists in the current database.
IF OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.Customers', N'U') IS NOT NULL BEGIN PRINT 'Table Exists' END
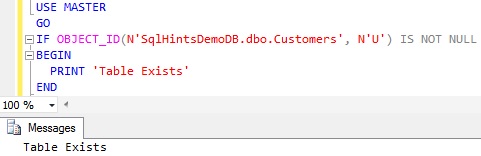
Specifying the Database Name and Schema Name parts for the Table Name is optional. But specifying Database Name and Schema Name provides an option to check the existence of the table in the specified database and within a specified schema, instead of checking in the current database across all the schemas. The below query shows that even though the current database is MASTER database, we can check the existence of the Customers table in the dbo schema in the SqlHintsDemoDB database.
USE MASTER GO IF OBJECT_ID(N'SqlHintsDemoDB.dbo.Customers', N'U') IS NOT NULL BEGIN PRINT 'Table Exists' END
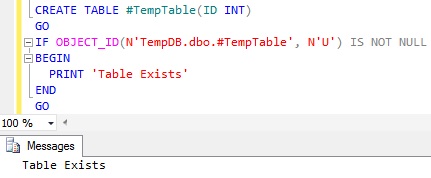
Pros: Easy to remember. One other notable point to mention about OBJECT_ID() function is: it provides an option to check the existence of the Temporary Table which is created in the current connection context. All other Approaches checks the existence of the Temporary Table created across all the connections context instead of just the current connection context. Below query shows how to check the existence of a Temporary Table using OBJECT_ID() function:
CREATE TABLE #TempTable(ID INT) GO IF OBJECT_ID(N'TempDB.dbo.#TempTable', N'U') IS NOT NULL BEGIN PRINT 'Table Exists' END GO
[ALSO READ] How to check if a Database exists in Sql Server
Approach 3: Using sys.Objects Catalog View
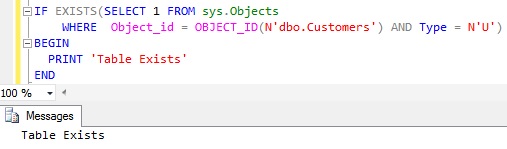
We can use the Sys.Objects catalog view to check the existence of the Table as shown below:
IF EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM sys.Objects
WHERE Object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.Customers')
AND Type = N'U')
BEGIN
PRINT 'Table Exists'
END
[ALSO READ] How to check if a record exists in a table
Approach 4: Using sys.Tables Catalog View
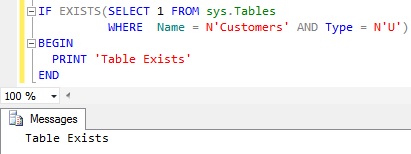
We can use the Sys.Tables catalog view to check the existence of the Table as shown below:
IF EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM sys.Tables
WHERE Name = N'Customers' AND Type = N'U')
BEGIN
PRINT 'Table Exists'
END
Sys.Tables catalog view inherits the rows from the Sys.Objects catalog view, Sys.objects catalog view is referred to as base view where as sys.Tables is referred to as derived view. Sys.Tables will return the rows only for the Table objects whereas Sys.Object view apart from returning the rows for table objects, it returns rows for the objects like: stored procedure, views etc.
[ALSO READ] How to check if a VIEW exists in Sql Server
Approach 5: Avoid Using sys.sysobjects System table
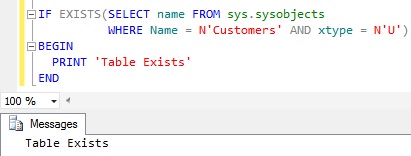
We should avoid using sys.sysobjects System Table directly, direct access to it will be deprecated in some future versions of the Sql Server. As per Microsoft BOL link, Microsoft is suggesting to use the catalog views sys.objects/sys.tables instead of sys.sysobjects system table directly.
IF EXISTS(SELECT name FROM sys.sysobjects
WHERE Name = N'Customers' AND xtype = N'U')
BEGIN
PRINT 'Table Exists'
END
[ALSO READ] :
How to check if a Database exists
How to check if a Stored Procedure exists in Sql Server
How to check if a View exists
How to check if Temp table exists
How to check if a record exists in table
what if I want to check through query that – if there is a database or not on remote server?
Thank you – very helpful. I have used the OBJECT_ID approach to check existence of temporary table created using variable values for the name, and it has worked perfectly.
IF OBJECT_ID(N'[Datastore].[dbo].[Header_’ + @PAY + ‘]’, N’U’) IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
PRINT ‘Table Header_’ + @PAY + ‘ has been created’
END
ELSE
BEGIN
PRINT ‘*** Table Header_’ + @PAY + ‘ has NOT been created ***’
END
what are the “N”s in the statement
WHERE Name = N’Customers’ AND xtype = N’U’
I want to know what N’ stands for as well
They indicate that the string literal following them can contain high Unicode characters, similar to the difference between varchar and nvarchar.
For Example:
DECLARE @UnicodeString nvarchar(50)
SET @UnicodeString = ‘Without the N these are unknown: ʢ Ͳ’
SELECT @UnicodeString
SET @UnicodeString = N’With the N you can see them: ʢ Ͳ’
SELECT @UnicodeString