FORMAT is one of the new built-in String Function introduced as a Part of Sql Server 2012. It returns the value formatted in the specified format using the optional culture parameter value. It is not an Sql Server native function instead it is .NET CLR dependent function.
SYNTAX: FORMAT ( value, format [, culture ] )
| Parameter | Description |
| value: | Value to be formatted |
| format: | This parameter specifies the format in which the vlaue will be formatted. |
| culture: | This parameter is optional, it specifies the culture in which the value is formatted. If it is not specified then the language of the current session is used. |
RETURNS: Return value type is nvarchar.
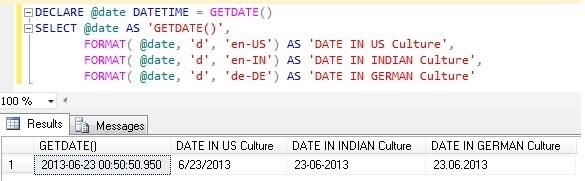
Example 1: FORMAT DATE with Culture
DECLARE @date DATETIME = GETDATE()
SELECT @date AS 'GETDATE()',
FORMAT( @date, 'd', 'en-US') AS 'DATE IN US Culture',
FORMAT( @date, 'd', 'en-IN') AS 'DATE IN INDIAN Culture',
FORMAT( @date, 'd', 'de-DE') AS 'DATE IN GERMAN Culture'
Result:
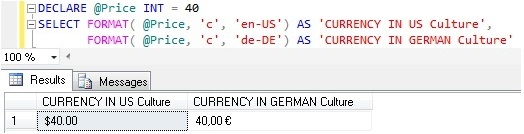
Example 2: FORMAT CURRENCY with Culture
DECLARE @Price INT = 40
SELECT FORMAT(@Price,'c','en-US')
AS 'CURRENCY IN US Culture',
FORMAT(@Price,'c','de-DE')
AS 'CURRENCY IN GERMAN Culture'
Result:
Example 3: FORMAT CURRENCY
DECLARE @Price DECIMAL(5,3) = 40.356
SELECT FORMAT( @Price, 'C') AS 'Default',
FORMAT( @Price, 'C0') AS 'With 0 Decimal',
FORMAT( @Price, 'C1') AS 'With 1 Decimal',
FORMAT( @Price, 'C2') AS 'With 2 Decimal',
FORMAT( @Price, 'C3') AS 'With 3 Decimal'
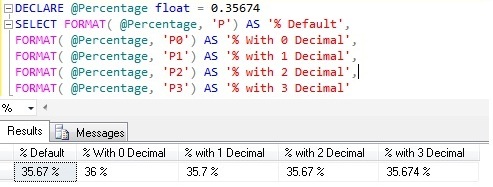
Example 4: FORMAT PERCENTAGE
DECLARE @Percentage float = 0.35674
SELECT FORMAT( @Percentage, 'P') AS '% Default',
FORMAT( @Percentage, 'P0') AS '% With 0 Decimal',
FORMAT( @Percentage, 'P1') AS '% with 1 Decimal',
FORMAT( @Percentage, 'P2') AS '% with 2 Decimal',
FORMAT( @Percentage, 'P3') AS '% with 3 Decimal'
Example 5: FORMAT NUMBER
DECLARE @Number AS DECIMAL(10,2) = 454545.389
SELECT FORMAT( @Number, 'N','en-US') AS 'Number Format in US',
FORMAT( @Number, 'N','en-IN') AS 'Number Format in INDIA'
SELECT FORMAT( @Number, '#.0') AS 'With 1 Decimal',
FORMAT( @Number, '#.00') AS 'With 2 Decimal',
FORMAT( @Number, '#,##.00') AS 'With Comma and 2 Decimal',
FORMAT( @Number, '##.00') AS 'Without Comma and 2 Decimal'
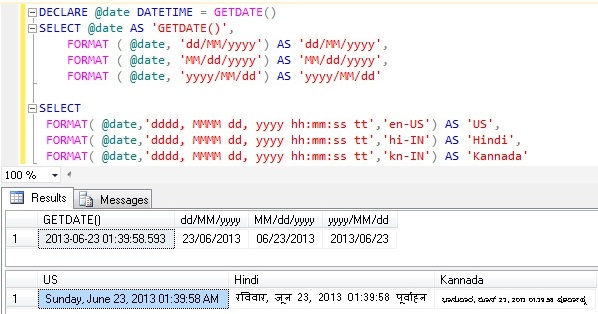
Example 6: CUSTOM DATE FORMATS
DECLARE @date DATETIME = GETDATE()
SELECT @date AS 'GETDATE()',
FORMAT ( @date, 'dd/MM/yyyy') AS 'dd/MM/yyyy',
FORMAT ( @date, 'MM/dd/yyyy') AS 'MM/dd/yyyy',
FORMAT ( @date, 'yyyy/MM/dd') AS 'yyyy/MM/dd'
SELECT
FORMAT( @date,'dddd, MMMM dd, yyyy hh:mm:ss tt','en-US')
AS 'US',
FORMAT( @date,'dddd, MMMM dd, yyyy hh:mm:ss tt','hi-IN')
AS 'Hindi',
FORMAT( @date,'dddd, MMMM dd, yyyy hh:mm:ss tt','kn-IN')
AS 'Kannada'
Result:
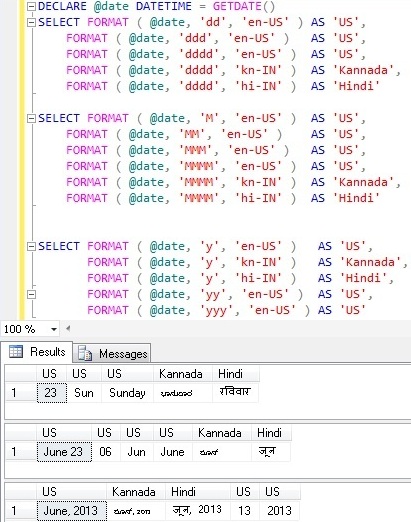
DECLARE @date DATETIME = GETDATE()
SELECT FORMAT ( @date, 'dd', 'en-US' ) AS 'US',
FORMAT ( @date, 'ddd', 'en-US' ) AS 'US',
FORMAT ( @date, 'dddd', 'en-US' ) AS 'US',
FORMAT ( @date, 'dddd', 'kn-IN' ) AS 'Kannada',
FORMAT ( @date, 'dddd', 'hi-IN' ) AS 'Hindi'
SELECT FORMAT ( @date, 'M', 'en-US' ) AS 'US',
FORMAT ( @date, 'MM', 'en-US' ) AS 'US',
FORMAT ( @date, 'MMM', 'en-US' ) AS 'US',
FORMAT ( @date, 'MMMM', 'en-US' ) AS 'US',
FORMAT ( @date, 'MMMM', 'kn-IN' ) AS 'Kannada',
FORMAT ( @date, 'MMMM', 'hi-IN' ) AS 'Hindi'
SELECT FORMAT ( @date, 'y', 'en-US' ) AS 'US',
FORMAT ( @date, 'y', 'kn-IN' ) AS 'Kannada',
FORMAT ( @date, 'y', 'hi-IN' ) AS 'Hindi',
FORMAT ( @date, 'yy', 'en-US' ) AS 'US',
FORMAT ( @date, 'yyy', 'en-US' ) AS 'US'
Result:
Example 7: Invalid Culture
DECLARE @date DATETIME = GETDATE() SELECT FORMAT(@date,'d','Test') AS 'Invalid Culture'
Result:
Msg 9818, Level 16, State 1, Line 2
The culture parameter ‘Test’ provided in the function call is not supported.
You may like to read the below new built-in function’s introduced in Sql Server 2012:
| New Built in Functions introduced in Sql Server | |||||||||||||||
| CONVERSION FUNCTIONS | |||||||||||||||
| PARSE | TRY_PARSE | ||||||||||||||
| TRY_CONVERT | |||||||||||||||
| STRING FUNCTIONS | |||||||||||||||
| CONCAT | FORMAT
| LOGICAL FUNCTIONS |
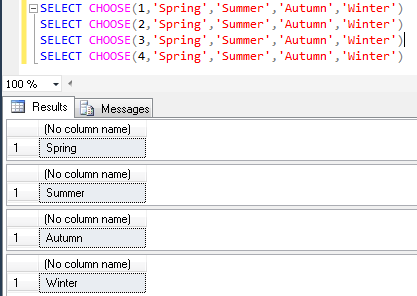
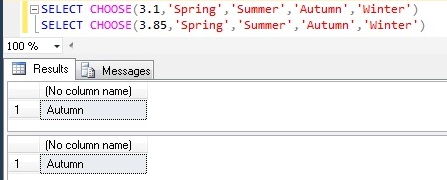
CHOOSE |
IIF
| DATE AND TIME FUNCTIONS |
EOMONTH |
DATEFROMPARTS |
DATETIMEFROMPARTS
| SMALLDATETIMEFROMPARTS |
DATETIME2FROMPARTS
| TIMEFROMPARTS |
DATETIMEOFFSETFROMPARTS
| | |||