In this article we will discuss on when we get the error like below in Sql Server and how to resolve it.
Msg 4712, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
Cannot truncate table ‘Customer’ because it is being referenced by a FOREIGN KEY constraint.
To demonstrate this error let us first create a demo db ‘SqlhintsTruncateDemo’, two tables Customer and Order.
CREATE DATABASE SqlhintsTruncateDemo GO USE SqlhintsTruncateDemo GO CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Customer] ( [CustID] [int] IDENTITY (1, 1) NOT NULL , CONSTRAINT [PK_Customer] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED ( [CustID] ) ) GO CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Order] ( [OrderID] [int] IDENTITY (1, 1) NOT NULL , [CustID] [int] NOT NULL , CONSTRAINT [PK_Order] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED ( [OrderID] ), CONSTRAINT [FK_Order_Customer] FOREIGN KEY ( [CustID] ) REFERENCES [dbo].[Customer] ( [CustID] ) ) GO
[ALSO READ] Truncate all/all except few/specified Tables of a Database in Sql Server
In the above script we have created a foreign key constraint FK_Order_Customer on the CustID column of the Order table which is referring to the CustID primary key column of the Customer table.
Disclaimer: As TRUNCATE table removes all the records from the table. Be careful before issuing this command.
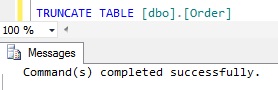
Now try to truncate the Order Table
TRUNCATE TABLE [dbo].[Order]
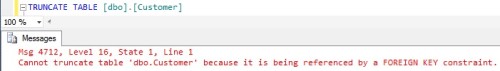
As per the above result truncation of the Order table is successful. Now try to truncate the Customer Table
TRUNCATE TABLE [dbo].[Customer]
As per the result the truncation of the Customer table is failing, because the
CustID column of the Customer table is referenced by the CustID column of the Order Table.
If we still want to Truncate the table, then we have to drop all the foreign key
constraints which are referring to the table to be truncated.
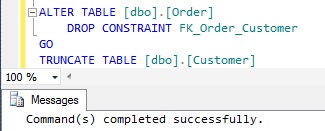
So now drop the foreign key constraint FK_Order_Customer and then try truncating
the Customer table.
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[Order] DROP CONSTRAINT FK_Order_Customer GO TRUNCATE TABLE [dbo].[Customer] GO
As per the above result it is clear that now the table truncation is successful after dropping all the foreign key constraints which are refering to the table to be truncated.
SELECT OBJECT_NAME (FK.referenced_object_id) 'Referenced Table', OBJECT_NAME(FK.parent_object_id) 'Referring Table', FK.name 'Foreign Key', COL_NAME(FK.referenced_object_id, FKC.referenced_column_id) 'Referenced Column', COL_NAME(FK.parent_object_id,FKC.parent_column_id) 'Referring Column' FROM sys.foreign_keys AS FK INNER JOIN sys.foreign_key_columns AS FKC ON FKC.constraint_object_id = FK.OBJECT_ID WHERE OBJECT_NAME (FK.referenced_object_id) = 'Enter Table Name'
In the above script replace the string ‘Enter Table Name’ with the table name for which you want to find out the referencing tables and the refering foreign key constraint name.
[ALSO READ] Truncate all/all except few/specified Tables of a Database in Sql Server