Many a times we come across a scenario where we get an input string with leading and/or trailing spaces. In such scenarios we would like to store it into the database by removing the leading and trailing spaces. But Microsoft doesn’t have a built-in TRIM function which can remove both leading and Trailing spaces.
Instead it has LTRIM function which can be used to remove leading blanks and RTRIM function which can be used to remove trailing spaces. Let us understand these functions with examples and then see how we can nest these two functions together as shown in the below examples to remove leading and trailing spaces.
LTRIM Function
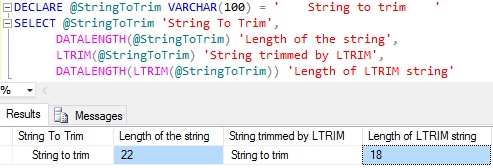
LTRIM function removes the leading spaces from the input string
DECLARE @StringToTrim VARCHAR(100) = ' String to trim ' SELECT @StringToTrim 'String To Trim', DATALENGTH(@StringToTrim) 'Length of the string', LTRIM(@StringToTrim) 'String trimmed by LTRIM', DATALENGTH(LTRIM(@StringToTrim)) 'Length of LTRIM string'
From the above result we can see that the LTRIM function is removing only the leading spaces. That is it has removed only the leading 4 spaces and not the trailing 4 spaces.
[ALSO READ] Difference between Len() and Datalength() functions in Sql Server
RTRIM Function
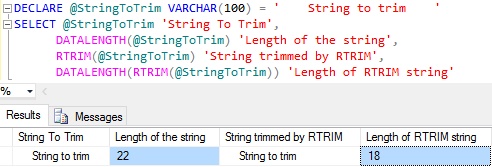
RTRIM function removes the trailing spaces from the input string
DECLARE @StringToTrim VARCHAR(100) = ' String to trim ' SELECT @StringToTrim 'String To Trim', DATALENGTH(@StringToTrim) 'Length of the string', RTRIM(@StringToTrim) 'String trimmed by RTRIM', DATALENGTH(RTRIM(@StringToTrim)) 'Length of RTRIM string'
From the above result we can see that the RTRIM function is removing only the trailing spaces. That is it has removed only the trailing 4 spaces and not the leading 4 spaces.
[ALSO READ] Usage of Function on Index Column in WHERE Caluse Leads to Index/Table Scan
TRIM Function
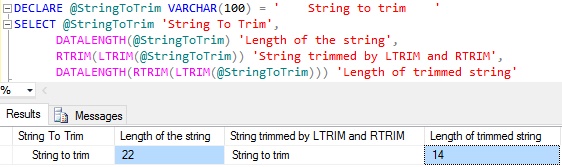
To remove the leading and trailing spaces we can nest the above LTRIM and RTRIM functions as shown in the below example:
DECLARE @StringToTrim VARCHAR(100) = ' String to trim ' SELECT @StringToTrim 'String To Trim', DATALENGTH(@StringToTrim) 'Length of the string', RTRIM(LTRIM(@StringToTrim)) 'String trimmed by LTRIM and RTRIM', DATALENGTH(RTRIM(LTRIM(@StringToTrim))) AS 'Length of trimmed string'
From the above result we can see that the nested use of RTRIM and LTRIM functions has removed both the leading and trailing paces.. That is it has removed both the leading 4 spaces and the trailing 4 spaces from the input string.
We can create a user defined function like the below one. And use it wherever we want to remove both leading and trailing spaces.
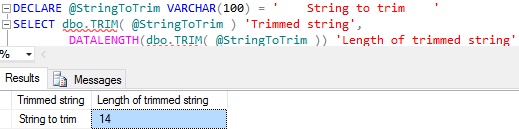
CREATE FUNCTION dbo.TRIM(@StringToTrim VARCHAR(MAX)) RETURNS VARCHAR(MAX) BEGIN RETURN RTRIM(LTRIM(@StringToTrim)) END
Below example shows how we can use the above created user defined TRIM function:
DECLARE @StringToTrim VARCHAR(100) = ' String to trim ' SELECT dbo.TRIM( @StringToTrim ) 'Trimmed string', DATALENGTH(dbo.TRIM( @StringToTrim )) AS 'Length of trimmed string'