This article presents how we can generate a script to truncate all tables/all tables except few specified tables/specified tables of a Database in Sql Server.
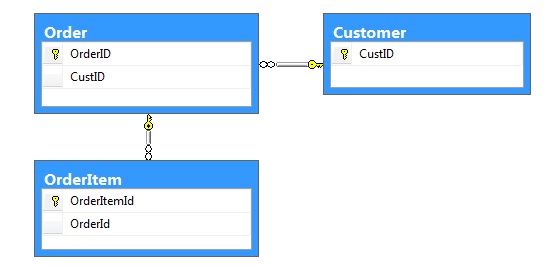
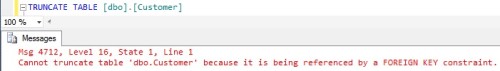
One of major the problem with table truncation is, we need to remove if there are any foreign key’s defined in other tables which references the columns in the table to be truncated. So to truncate a table we need to first remove all the foreign key references then truncate the table and finally add back the removed foreign key constraints.
Let us first create a demo database with sample tables as shown in the below image by the by the following script:
--Create demo database with tables having foreign
--key relations between them and sample data in it
SET NOCOUNT ON
GO
CREATE DATABASE SqlhintsTruncateDBDemo
GO
USE SqlhintsTruncateDBDemo
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Customer] (
[CustID] [int] NOT NULL ,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Customer] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
( [CustID] )
)
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Order] (
[OrderID] [int] NOT NULL ,
[CustID] [int] NOT NULL ,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Order] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
( [OrderID] ),
CONSTRAINT [FK_Order_Customer] FOREIGN KEY
( [CustID] ) REFERENCES [dbo].[Customer] (CustID)
)
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[OrderItem] (
[OrderItemId] [int] NOT NULL ,
[OrderId] [int] NOT NULL ,
CONSTRAINT [PK_OrderItem] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
( [OrderItemId] ),
CONSTRAINT [FK_OrderItem_Order] FOREIGN KEY
([OrderId]) REFERENCES [dbo].[Order] ([OrderId])
)
GO
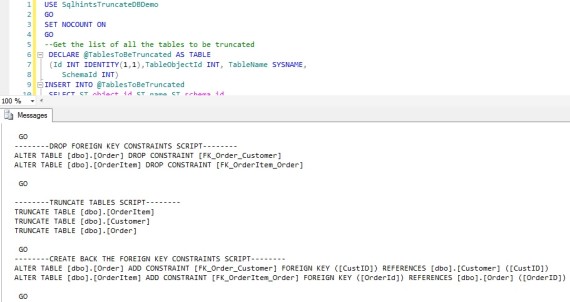
We can use the below script to generate the script to truncate all the tables of a database.
USE SqlhintsTruncateDBDemo
GO
SET NOCOUNT ON
GO
--Get the list of all the tables to be truncated
DECLARE @TablesToBeTruncated AS TABLE
(Id INT IDENTITY(1,1),TableObjectId INT, TableName SYSNAME,
SchemaId INT)
INSERT INTO @TablesToBeTruncated
SELECT ST.object_id,ST.name,ST.schema_id
FROM sys.Tables ST
WHERE ST.type = 'U' AND ST.NAME NOT LIKE '#%'
AND ST.name <> 'sysdiagrams'
--AND ST.NAME NOT IN ('') -- Specify here the comma separated table names for which truncation is not required
--AND ST.NAME IN ('') -- Specify here the comma separated table names which needs to be truncated
--Generate the foreignkeys drop and create back script
DECLARE @CreateScript AS NVARCHAR(MAX), @DropScript AS NVARCHAR(MAX)
SELECT
------------DROP SCRIPT--------------------
@DropScript = ISNULL(@DropScript,'') + 'ALTER TABLE ' + QUOTENAME(SCHEMA_NAME(Tlist.SchemaId)) + '.'
+ QUOTENAME(OBJECT_NAME(FKey.parent_object_id)) + ' DROP CONSTRAINT ' + QUOTENAME(FKey.name)
+ CHAR(10),
-----------CREATE BACK SCRIPT-------------
@CreateScript = ISNULL(@CreateScript,'') + 'ALTER TABLE ' + QUOTENAME(SCHEMA_NAME(Tlist.SchemaId)) + '.'
+ QUOTENAME(OBJECT_NAME(FKey.parent_object_id)) + ' ADD CONSTRAINT ' + QUOTENAME(FKey.name)
+ ' FOREIGN KEY ' + '(' + STUFF(( -- Get the list of columns
SELECT ',' + QUOTENAME(COL_NAME(FKeyCol.parent_object_id, FKeyCol.parent_column_id))
FROM SYS.FOREIGN_KEY_COLUMNS FKeyCol
WHERE FKey.OBJECT_ID = FKeyCol.constraint_object_id
ORDER BY FKeyCol.constraint_column_id
FOR XML PATH('')),1,1,'') + ')'
+ ' REFERENCES ' + QUOTENAME(SCHEMA_NAME(Tlist.SchemaId)) + '.'
+ QUOTENAME(OBJECT_NAME(FKey.referenced_object_id)) + ' (' + STUFF(( -- Get the list of columns
SELECT ',' + QUOTENAME(COL_NAME(FKeyCol.referenced_object_id, FKeyCol.referenced_column_id))
FROM SYS.FOREIGN_KEY_COLUMNS FKeyCol
WHERE FKey.OBJECT_ID = FKeyCol.constraint_object_id
ORDER BY FKeyCol.constraint_column_id
FOR XML PATH('')),1,1,'') + ') '
+ CASE WHEN update_referential_action_desc = 'CASCADE' THEN ' ON UPDATE CASCADE'
WHEN update_referential_action_desc = 'SET_DEFAULT' THEN ' ON UPDATE SET DEFAULT'
WHEN update_referential_action_desc = 'SET_NULL' THEN ' ON UPDATE SET NULL'
ELSE ''
END
+ CASE WHEN delete_referential_action_desc = 'CASCADE' THEN ' ON DELETE CASCADE'
WHEN delete_referential_action_desc = 'SET_DEFAULT' THEN ' ON DELETE SET DEFAULT'
WHEN delete_referential_action_desc = 'SET_NULL' THEN ' ON DELETE SET NULL'
ELSE ''
END + CHAR(10)
FROM @TablesToBeTruncated Tlist
INNER JOIN SYS.FOREIGN_KEYS FKey
ON Tlist.TableObjectId = FKey.referenced_object_id
--PRINT THE TRUNCATION SCRIPT
IF LEN(ISNULL(@DropScript,'')) > 0
BEGIN
PRINT CHAR(10) + ' GO ' + CHAR(10) + '--------DROP FOREIGN KEY CONSTRAINTS SCRIPT--------'
PRINT @DropScript + CHAR(10) + ' GO ' + CHAR(10)
END
PRINT '--------TRUNCATE TABLES SCRIPT--------'
--TRUNCATE TABLES
DECLARE @id INT,@truncatescript NVARCHAR(MAX)
SELECT @id = MIN(Id)FROM @TablesToBeTruncated
WHILE @id is not null
BEGIN
SELECT @truncatescript = 'TRUNCATE TABLE ' + QUOTENAME(SCHEMA_NAME(SchemaId)) + '.' + QUOTENAME(TableName)
FROM @TablesToBeTruncated WHERE Id = @id
PRINT @truncatescript
SELECT @id = MIN(Id)FROM @TablesToBeTruncated WHERE Id > @id
END
IF LEN(ISNULL(@CreateScript,'')) > 0
BEGIN
PRINT CHAR(10) + ' GO ' + CHAR(10) + '--------CREATE BACK THE FOREIGN KEY CONSTRAINTS SCRIPT--------'
PRINT CAST((@CreateScript + CHAR(10) + ' GO ' + CHAR(10)) AS NTEXT)
END
GO
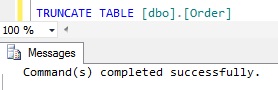
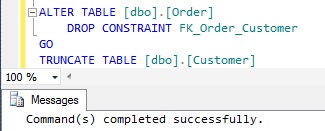
Below is the result of executing the above script:
Disclaimer: As TRUNCATE table removes all the records from the table permanently. So, think twice before executing the truncate table statement.
By default the above script generates the script to truncate all the tables of a database. If need is to truncate only the specified tables then uncomment the line number 15 (i.e.–AND ST.NAME IN (”)) in the above script and mention the list of tables to be truncated. And if requirement is to truncate all the tables except few tables, then uncomment only the line number 14 (i.e. –AND ST.NAME NOT IN (”)) in the above script and mention the list of tables which shouldn’t be considered for truncation.