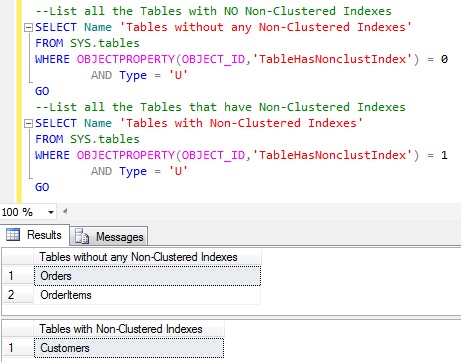
We can write a query like below to get all the Tables without any Non-Clustered indexes:
--List all the Tables with NO Non-Clustered Indexes SELECT Name 'Tables without any Non-Clustered Indexes' FROM SYS.tables WHERE OBJECTPROPERTY(OBJECT_ID,'TableHasNonclustIndex') = 0 AND Type = 'U'
We can write a query like below to get all the Tables with Non-Clustered indexes:
--List all the Tables that have Non-Clustered Indexes SELECT Name 'Tables with Non-Clustered Indexes' FROM SYS.tables WHERE OBJECTPROPERTY(OBJECT_ID,'TableHasNonclustIndex') = 1 AND Type = 'U'
Let us understand this with example:
CREATE DATABASE SqlHintsDemoDB GO USE SqlHintsDemoDB GO /*Let us create Customers table with Clustered and Non-Clustered Indexes.*/ CREATE TABLE dbo.Customers ( CustomerId int IDENTITY (1, 1) PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED NOT NULL, FirstName Varchar(50), LastName Varchar(50)) GO CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX IX_Customers ON dbo.Customers(FirstName,LastName) GO /*Let us create Orders Table with Clustered indexe only.*/ CREATE TABLE dbo.Orders ( OrderId int IDENTITY (1, 1) PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED NOT NULL, CustomerId int NOT NULL , CreationDT DATETIME NOT NULL) GO /*Let us create OrderItems Table without any indexes.*/ CREATE TABLE dbo.OrderItems ( OrderItemId int IDENTITY (1, 1), OrderId int NOT NULL, Qty int NOT NUll) GO
Now let us run the queries to get the list of all Tables with or without Non-Clustered indexes and verify the result:
why we have only one clustered index in per table in sql
As the table data is sorted and stored in the order of the clustered index key.