Frequently, we come across a scenario where we need to check the existence of a record and based on it perform some action. This article explains how to use the EXISTS clause to check the existence of a record in a table. There are multiple options for checking the existence of a record, but EXISTS clause is the best option in terms performance. Basically the Exists clause checks the existence of a record and it stops processing further records after finding the first instance of the record which matches the criteria
This article covers the following examples:
- Using EXISTS clause in the IF statement to check the existence of a record
- Using EXISTS clause in the CASE statement to check the existence of a record
- Using EXISTS clause in the WHERE clause to check the existence of a record
- EXISTS clause having subquery joining multiple tables to check the record existence in multiple tables
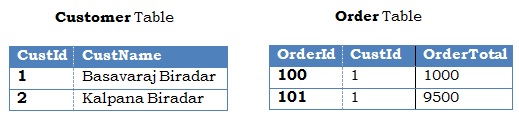
To demonstrate this let us create a Customer and Order table as shown in the below image by the following script:
USE TEMPDB GO --Create Customer Table CREATE TABLE dbo.Customer (CustId INT, CustName NVARCHAR(50)) --Create Order Table CREATE TABLE dbo.[Order] (OrderId INT, CustId INT, OrderTotal Money) GO --Insert sample records into Customer table INSERT INTO dbo.Customer VALUES(1, 'Basavaraj Biradar'), (2,'Kalpana Biradar') --Insert sample records into Customer table INSERT INTO dbo.[Order] VALUES(100,1, 1000), (101,1,9500) GO
[ALSO READ] How to check if a Database exists
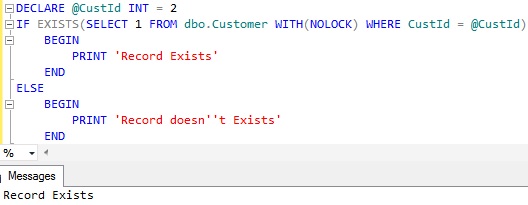
EXAMPLE 1: Using EXISTS clause in the IF statement to check the existence of a record
Below example script checks the existence of the customer record with CustId = 2 in the IF statement
DECLARE @CustId INT = 2
IF EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM dbo.Customer WITH(NOLOCK)
WHERE CustId = @CustId)
BEGIN
PRINT 'Record Exists'
END
ELSE
BEGIN
PRINT 'Record doesn''t Exists'
END
[ALSO READ] How to check if a Table exists
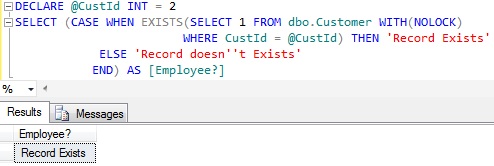
EXAMPLE 2: Using EXISTS clause in the CASE statement to check the existence of a record
DECLARE @CustId INT = 2
SELECT (CASE WHEN EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM dbo.Customer WITH(NOLOCK)
WHERE CustId = @CustId) THEN 'Record Exists'
ELSE 'Record doesn''t Exists' END) AS [Employee?]
[ALSO READ] How to check if Temp table exists
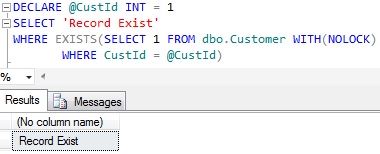
EXAMPLE 3: Using EXISTS clause in the WHERE clause to check the existence of a record
DECLARE @CustId INT = 1
SELECT 'Record Exist'
WHERE EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM dbo.Customer WITH(NOLOCK)
WHERE CustId = @CustId)
[ALSO READ] How to check if a Stored Procedure exists in Sql Server
EXAMPLE 4: EXISTS clause having sub query joining multiple tables to check the record existence in multiple tables
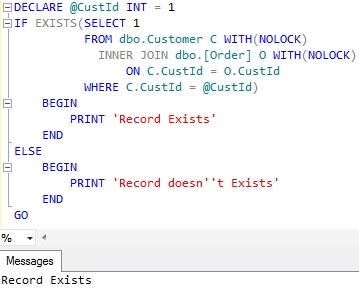
DECLARE @CustId INT = 1
IF EXISTS(SELECT 1
FROM dbo.Customer C WITH(NOLOCK)
INNER JOIN dbo.[Order] O WITH(NOLOCK)
ON C.CustId = O.CustId
WHERE C.CustId = @CustId)
BEGIN
PRINT 'Record Exists'
END
ELSE
BEGIN
PRINT 'Record doesn''t Exists'
END
GO
[ALSO READ] :
How to check if a Database exists
How to check if a Table exists
How to check if a Stored Procedure exists in Sql Server
How to check if a View exists
How to check if Temp table exists
I enjoyed reading this article.
Good and simple examples of EXISTS.
I ran all the four statements and working fine
For few statements I changed not exiting id in the table and
ran which displayed
‘Record doesn”t Exists’
Please keep publishing some more examples.
Write an article on frequently used
sp_xxx,
DBCC,
sys.xxxxx
CONSTRAINTS
commands in day to day developer work.
Thanks a lot for educating the community
with examples
Thank you Kris
What if the input is dynamic?
The above code is for pre-defined input.
So how to write a query for that?