Data Manipulation Language (DML) Triggers have access to the two special logical Tables named INSERTED and DELETED. These are the temporary tables managed by Sql Server. Structure of these tables will be same as that of the table on which the DML action is fired and holds the old and new values of the rows which are modified by the DML statement.
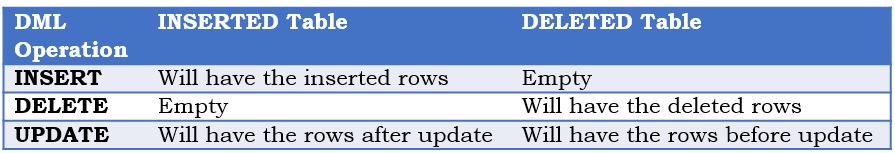
DELETED logical table will hold the rows which are deleted from the trigger table (i.e. the table on which the trigger is defined) by the DELETE or UPDATE operation. An UPDATE DML operation is internally executed as first the deletion of the existing record and then insertion of the new record.
INSERTED logical table will hold the rows which are inserted by the INSERT and UPDATE statement.
Below table depicts the contents of the INSERTED and DELETED logical tables for three DML operations
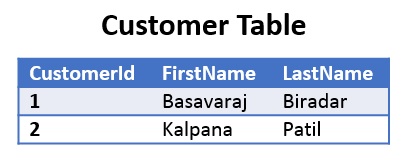
To understand INSERTED and DELETED logical tables with extensive list of examples let us create a Customer Table as shown in the following image by the following script:
--Create Demo Database
CREATE DATABASE SqlHintsLogicalTablesDemo
GO
USE SqlHintsLogicalTablesDemo
GO
--Create Customer Table
CREATE TABLE Customer
( CustomerId INT IDENTITY (1, 1) NOT NULL ,
FirstName NVARCHAR(50), LastName NVARCHAR(50))
GO
--Add sample records
INSERT INTO dbo.Customer ( FirstName, LastName )
VALUES('Basavaraj','Biradar'),
('Kalpana','Patil')
Let us create a AFTER trigger INSERTEDAndDELETEDTableExample on the Customer table for the triggering DML actions INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE by executing the following statement. This AFTER trigger is displaying the content of the INSERTED and DELETED logical tables
CREATE TRIGGER INSERTEDAndDELETEDTableExample
ON Customer
FOR INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
AS
BEGIN
PRINT '**********DELETED Table***************'
SELECT * FROM DELETED
PRINT '*********INSERTED Table***************'
SELECT * FROM INSERTED
END
INSERTED and DELETED Logical Tables behavior in-case of INSERT DML OPERATION
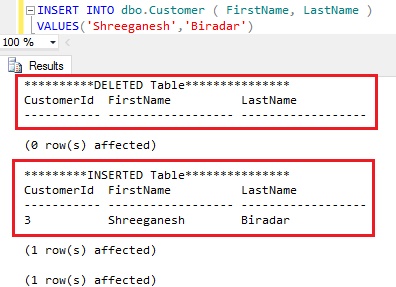
Execute the following INSERT statement to insert the record into the Customer table.
INSERT INTO dbo.Customer ( FirstName, LastName )
VALUES('Shreeganesh','Biradar')
From the result we can see that for the INSERT DML operation on the Customer table, no record is added to the DELETED logical table but the inserted record is available in the INSERTED logical table
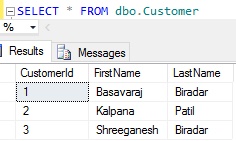
Let us check the records in the Customer table post the execution of the above INSERT statement
INSERTED and DELETED Logical Tables behavior in-case of DELETE DML OPERATION
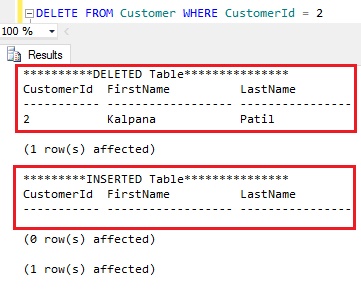
Execute the following DELETE statement to DELETE a record from the Customer table.
DELETE FROM Customer WHERE CustomerId = 2
From the result we can see that the record which is deleted from the Customer table from DELETE DML operation is available in the DELETED logical table and the INSERTED logical table is empty
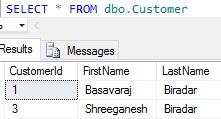
Let us check the records in the Customer table post the execution of the above DELETE statement
INSERTED and DELETED Logical Tables behavior in-case of UPDATE DML OPERATION
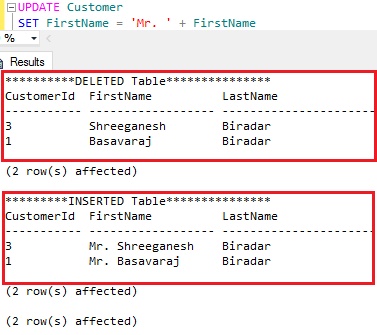
Execute the following UPDATE statement to update all the records from the Customer table.
UPDATE Customer SET FirstName = 'Mr. ' + FirstName
From the above result we can see that INSERTED table will have the records with values post update and the DELETED table will have the the records with a state prior to the update
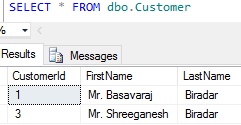
Let us check the records in the Customer table post the execution of the above UPDATE statement
Drop the trigger INSERTEDAndDELETEDTableExample by executing the following statement
DROP TRIGGER INSERTEDAndDELETEDTableExample