In NVARchar DataType column we can store both Single byte and Double byte data. Many a times we want to know how many records have Single byte or Double byte data. Let us understand this with an example.
CREATE DATABASE SqlHintsDemo GO USE SqlHintsDemo GO -- Create Customer Table which has NVARchar column CustomerName CREATE TABLE dbo.Customer (CustomerId int, CustomerName NVarchar(50)) GO --Populate Customer table with single byte and --double byte CustomerName records INSERT INTO dbo.Customer (CustomerId, CustomerName) VALUES (100, 'Basavaraj') INSERT INTO dbo.Customer (CustomerId, CustomerName) VALUES (200, N'尊敬卿') INSERT INTO dbo.Customer (CustomerId, CustomerName) VALUES (300, 'Biradar') GO
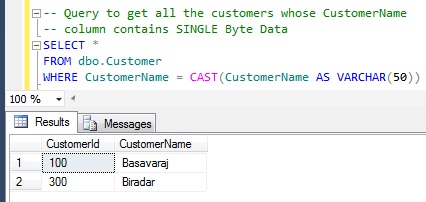
| Query to get all the Customers whose CustomerName column contains SINGLE Byte Data |
-- Query to get all the customers whose CustomerName -- column contains SINGLE Byte Data SELECT * FROM dbo.Customer WHERE CustomerName = CAST(CustomerName AS VARCHAR(50))
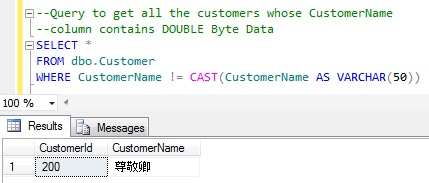
| Query to get all the Customers whose CustomerName column contains DOUBLE Byte Data |
--Query to get all the customers whose CustomerName --column contains DOUBLE Byte Data SELECT * FROM dbo.Customer WHERE CustomerName != CAST(CustomerName AS VARCHAR(50))
You may also like to read below other popular articles:
Difference Between Sql Server VARCHAR and NVARCHAR Data Type
Difference Between Sql Server VARCHAR and VARCHAR(MAX) Data Type
Difference between Sql Server Char and Varchar Data Type
Difference between DateTime and DateTime2 DataType
Please correct me, if my understanding is wrong. Comments are always welcome.